70% → 0%
Admin friction automated. Formatting, compliance, and documentation handled by the system so teachers don't have to.
Curate, Not Create
Teachers review context-aware AI suggestions instead of wrestling with blank canvases and open-ended prompts.
1 Persona, 1 UX
The interface adapts to each teacher's archetype and class profile—no two dashboards are the same.
The 70/30 Paradox
We ask teachers to be "inspirers," but we force them to be administrators. Research shows that modern educators spend roughly 70% of their time on administrative friction—planning, documentation, and formatting—leaving only 30% for actual creative teaching. This inefficiency is feeding a systemic burnout crisis.
The Competence-Capacity Gap
The issue isn't a lack of skill; it's a lack of bandwidth. My research revealed that 86% of teachers have high design confidence, yet 76% still default to static PowerPoints because they lack the time to use better tools. This "Admin Load" creates a barrier where teachers abandon creative ideas at the execution stage due to sheer decision fatigue.
The Design Goal
To build a system that automates the rigid 70% so teachers can reclaim their creative 30%. The design goal was to shift the interaction model from "Creation" (doing it yourself) to "Curation" (reviewing AI suggestions), thereby bridging the gap between a teacher's high potential and their limited time.
The Action Funnel: Where Intentions Fail
I analyzed the existing teacher workflow using the CREATE Action Funnel to pinpoint exactly where intentions were failing. The analysis revealed a critical drop-off at the "Execution" stage. Teachers had the 'Cue' (Lesson Idea) and 'Reaction' (Desire), but the 'Evaluation' (Effort required) caused them to abandon the task.
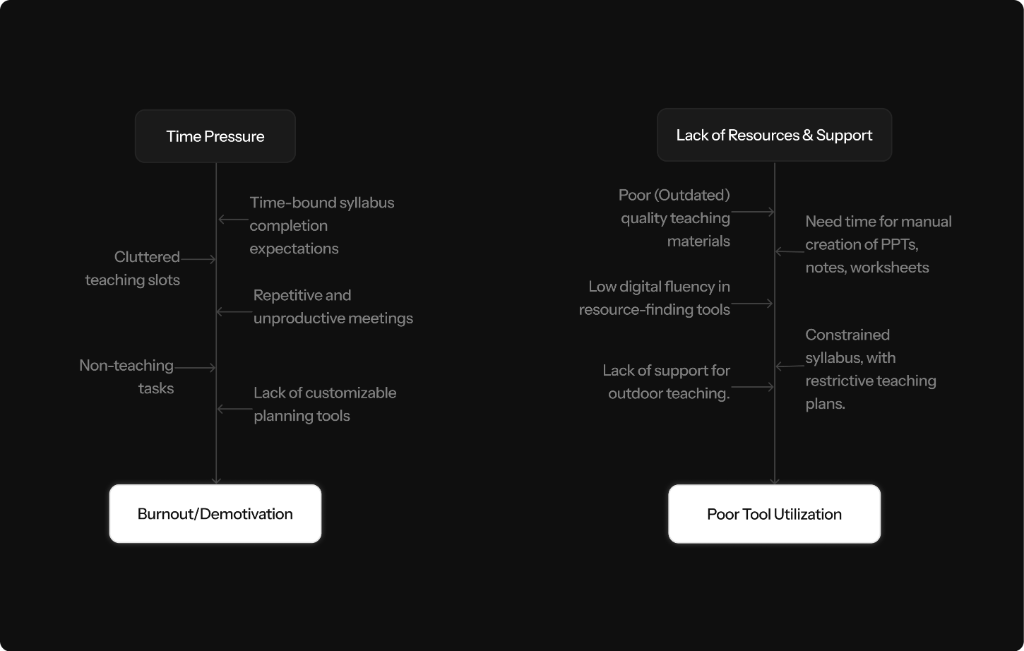
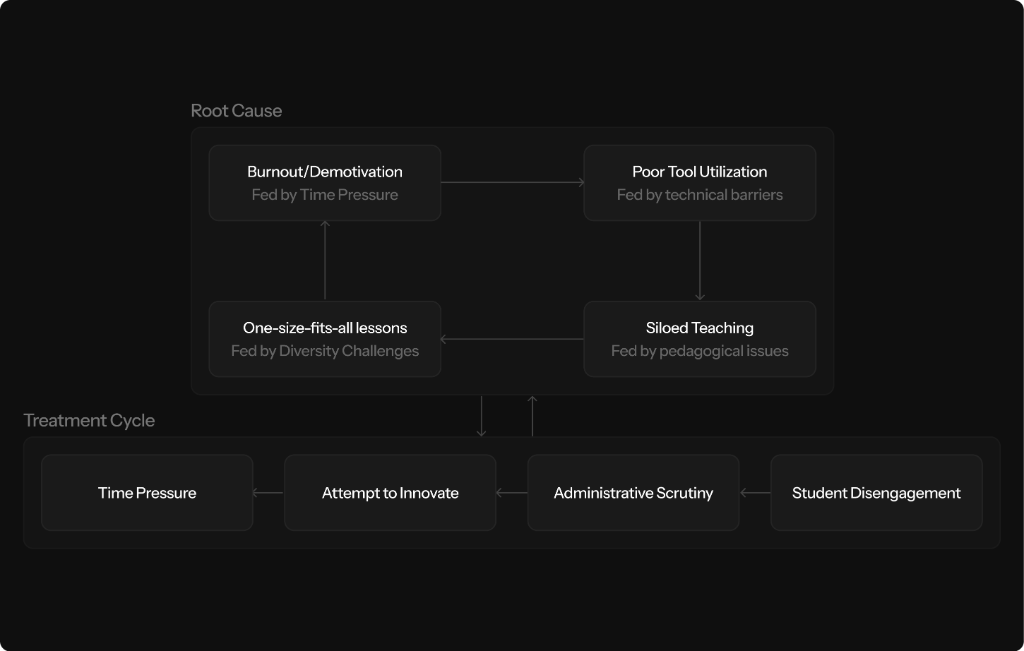
The Root Cause: Time Pressure & Siloed Teaching
We started by asking why teachers don't just "use better tools." By mapping the root causes, we discovered a web of interdependent blockers. Burnout isn't just about "too much work"—it's fed by rigid systems, lack of resources, and emotional fatigue. This meant Aurika couldn't just be a tool; it had to be an intervention.
This system feeds itself. Time Pressure fuels Burnout, which leads to Poor Utilization of Tools, resulting in Siloed Teaching. Aurika serves as the intervention point: by automating the "Time Pressure," we break the cycle before it reaches "Burnout."
What Teachers Actually Said
Numbers tell one story; voices tell another. I grouped interview insights into thematic clusters to understand the emotional toll behind the data. Three dominant patterns emerged around time pressure, innovation barriers, and lack of institutional support.
Time Pressure & Burnout
"I get very tired because I'm a science teacher—I have 24 slots, sometimes just 2 free."
The time limit for lesson planning and executing the entire flow of the plan within deadlines is a significant challenge.
Executing lesson plans within time constraints remains a core issue.
"Teachers have been reduced to 70% administrators, with only 30% of their essence remaining as educators."
Additional responsibilities assigned by school management reduce the time and energy available for creative lesson design.
Reduce time spent re-planning effective lesson plans just to meet arbitrary requirements.
Reducing non-teaching activities
Reduce paperwork and documentation
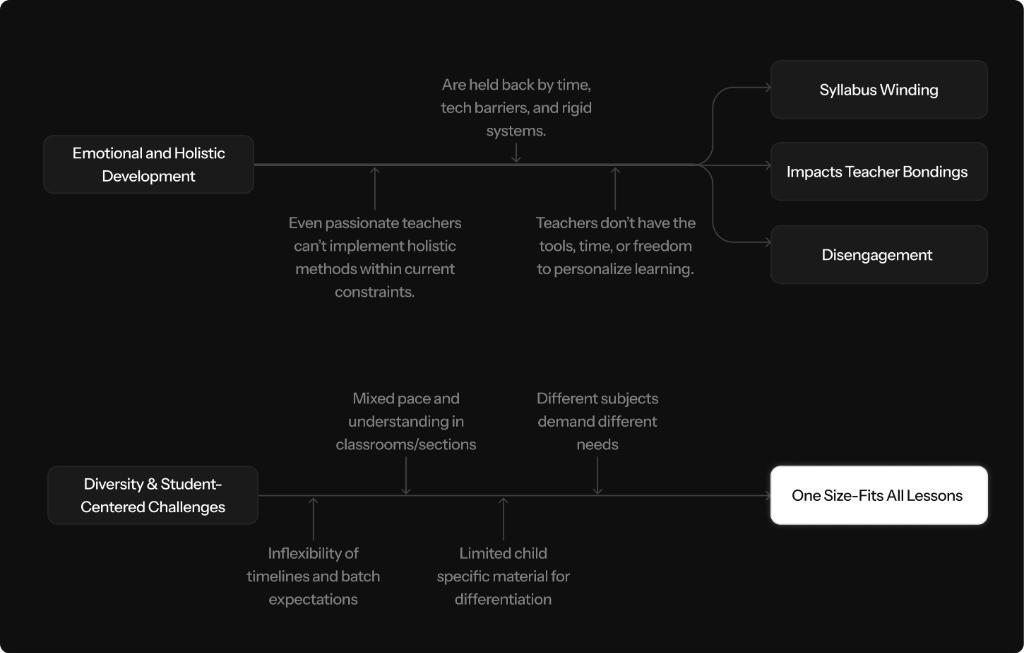
With so much time consumed by non-teaching tasks, the limited time left for actual teaching leaves teachers with no choice but to simply wind up the syllabus. This often means rushing through lessons without ensuring real understanding, just to stay on track with academic timelines.
Teachers typically begin each new session with strong enthusiasm for teaching, but over time, the growing load of non-instructional tasks dilutes their original intent. This shift not only dampens their motivation but also contributes to long-term fatigue and burnout.
Save time spent on resource creation and invest it in giving students meaningful, lasting learning experiences
Lack of Resources & Support
"Limited knowledge of computer tools makes it hard to create good visuals."
"I want notebook work to be removed; it takes most of our time."
Finding age-appropriate resources that align with children's developmental levels can be tricky.
Some topics are not relevant to the students' age group, reducing engagement.
Each topic is covered with basic detail, but lacks depth for exploration.
Adding solved questions that are both relevant and illustrative takes extra effort.
"Edurev helps me get worksheets, flashcards, and mnemonics for engaging teaching."
Doing the necessary research to back up the lesson content is time-consuming but essential.
Teachers are forced to improvise due to outdated, text-heavy NCERT materials that lack depth, visual engagement, and real-world connections — draining energy that should go toward pedagogy.
Rigid syllabus structures and lack of freedom restrict teachers from adapting content to student needs, while insufficient evaluation methods and tools limit creative lesson delivery.
Provide ready-made, visually rich, and adaptable teaching resources so teachers can focus on delivery rather than creation
Innovating Beyond Present
Activity-based teaching and fully practical methods
Avoid overemphasis on notebook work
Focus solely on overall development of students without distractions
Flexibility in content selection
More experiential learning instead of rote memorization
Replace rote learning with creative learning
Today's generation needs shorter, bite-sized content to stay engaged.
Collaborating with colleagues to brainstorm innovative teaching ideas is important to me.
Teachers overwhelmingly seek a shift from rote memorization to experiential, activity-based learning — with flexibility in content selection and methods that prioritize holistic student development.
There is a strong desire for interactive, bite-sized, and real-world connected content that goes beyond textbook rewrites, supported by collaborative planning and technology integration.
Enable teachers to deliver creative, hands-on, and experiential learning without building everything from scratch
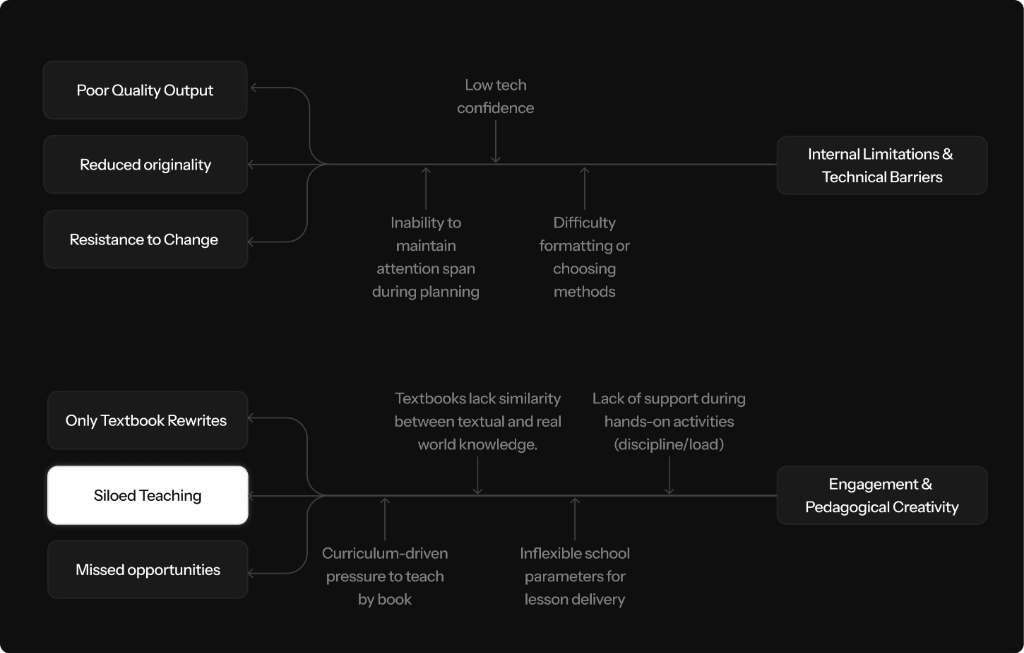
Internal Limitations & Technical Barriers
Ensuring that content is original and not copied takes additional creative effort.
I'm not facing any difficulty
"I've studied short courses like child psychology from Swayam to sharpen my teaching."
Integrating engaging comic-style visuals or pictures to make content appealing is a creative challenge.
"Formatting becomes difficult at times."
Maintaining focus and concentration throughout the design process can be difficult.
Balancing the learning capacities of every student while creating value-driven models that work for all is complex.
Adapting lessons to incorporate different teaching methods adds complexity to planning.
Teachers face a dual barrier: low digital proficiency makes formatting and visual creation difficult, while maintaining creative focus throughout the planning process drains cognitive energy.
The challenge of designing inclusive, engaging lessons for diverse learners is compounded by rigid systems that leave little room for creative adaptation or experimentation.
Lower the technical barrier for lesson creation so teachers can focus on pedagogy, not formatting
Diversity & Student-Centered Challenges
"I try to provide real-life case scenarios or examples from my own life."
There's often more content than can be covered in the limited class time, which creates a struggle in prioritization.
The content is age-appropriate and graspable for students.
"A, B, and C sections learn faster than D and E — but we are blamed either for rushing or for not completing the syllabus."
"This doesn't allow space for exploration."
"When you interact with kids, you understand different mindsets."
Make every student excited and eager to learn each day
Slow learners should have access to tools or devices that help them learn at their pace (e.g., a Doremon-like gadget)
Teachers struggle to serve diverse learning paces within rigid, one-size-fits-all school parameters — leading to blame for either rushing ahead or falling behind on syllabus coverage.
There is a deep desire to personalize learning and make every student feel capable, but the lack of adaptive tools and inflexible content structures make this nearly impossible at scale.
Design adaptive content and tools that let teachers differentiate instruction without multiplying their workload
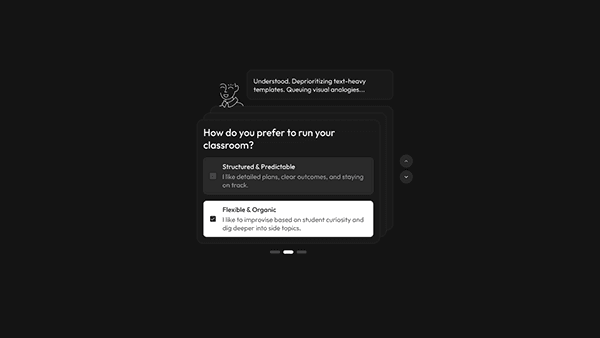
User Archetypes: The Juggler
"Teacher" is not a monolith. By mapping users on axes of Focus (Student vs. Personal) and Approach (Traditional vs. Progressive), I identified four distinct mindsets that require different UX strategies.
From Research to Rules
Before jumping into features, I distilled the research into three design principles that would govern every decision going forward.
1. Automate the Rigid, Protect the Creative
The 70/30 data made it clear: the system must absorb the mechanical work (formatting, compliance, documentation) so teachers can invest their energy in the 30% that actually matters—creative lesson design.
2. Curate, Don't Create
Teachers don't have the bandwidth to prompt, iterate, and refine AI output. The interaction model must shift from "creation" (blank canvas) to "curation" (reviewing pre-generated, context-aware suggestions).
3. Context Over Configuration
Rather than asking teachers to manually configure settings, the system should infer context from their behavior, subject, and class data—reducing setup time and decision fatigue before work even begins.
The Impact-Effort Matrix
Before jumping into design, I mapped every potential feature against two axes: user/business impact and engineering effort. This framework ensured we weren't just building what was exciting — we were building what would move the needle fastest.
- PPT Generator
- Activity Generator
- Real-Life Problem Solver
- Save to Library (Personal Vault)
- Personalization Engine
- Class Snapshot
- Visual Simulation Engine
- Lesson Plan Enhancer
- Worksheet/Question Generator
- Contextual Sidebar Suggestions
- Hook Generator
- Smart Summarizer
- Text Rewriter/Polisher
- Make it Relevant
- Insert & Replace Suggestions
- Differentiation Suggestions
- Class Profiler (Calibration Tags)
- Exit Ticket Generator
- Discussion Prompt Generator
- Reflection Nudges
- Peer Sharing Layer
- Collaborative Mode
- Advanced Analytics Dashboards
- Student Chatbots
- LMS Integrations
- Focus Mode (silence suggestions)
- Export Options (DOC/PDF/PPTX)
- Performance Tracking
- Error Handling & Fallbacks
The MVP Scope
From the Impact-Effort analysis, I carved the MVP into three tiers: The Foundation (core lesson tools), The Differentiators (what makes Aurika unique), and The Hygiene (minimum expectations). Everything else was scoped into the V2.0 roadmap.
The Aurika MVP (Launch Scope)
The complete ecosystem for the modern teacher.
The Foundation
- •Lesson Planner
- •Worksheet/Question Generator
- •Smart Summarizer
- •Text Rewriter/Polisher
- •Contextual Sidebar Suggestions
- •Hook Generator
- •Activity Generator
- •Real Life Problem Builder
- •Make it Relevant
The Differentiators
- •PPT Generator
- •Visual Simulation Engine
- •Class Snapshots
- •Save To Library
- •Adaptive Suggestions
- •Pattern Recognition
- •One-Solution Mode
- •Class Profile
- •Discussion Prompt Generator
- •Reflection Nudges
- •Exit Ticket Generator
The Hygiene
- •Proactive Call-Outs
- •Export Options
- •Error Handling & Fallbacks
Future Scope (V2.0)
Post-launch expansion.
- •Student Companion AI (Student Personalized Teaching)
- •Peer Sharing Layer
- •Collaborative Mode
- •Analytics Dashboards
- •Performance Tracking
The Aurika System: From Prioritization to Pattern
Research finding: Teachers overwhelmingly wanted tools to create faster, not tools to connect with peers. The survey data explicitly deprioritized "Social Features" (only 32% interest) in favor of Creation Tools.
Design response: We cut the planned "Community Feed" feature entirely to focus on the Simulation Engine and One-Click Presentation Generator.
Research finding: Teachers feel guilty assigning "busywork" (copying from the board) just to fill time, but they lack the resources to create engaging materials quickly.
Design response: Aurika's Automated Visual Aids shift the paradigm from "Dictation" to "Creation" — auto-converting text into visual worksheets, mind maps, and diagrams that fulfill learning outcomes without the boredom.
Leveraging Familiar Mental Models
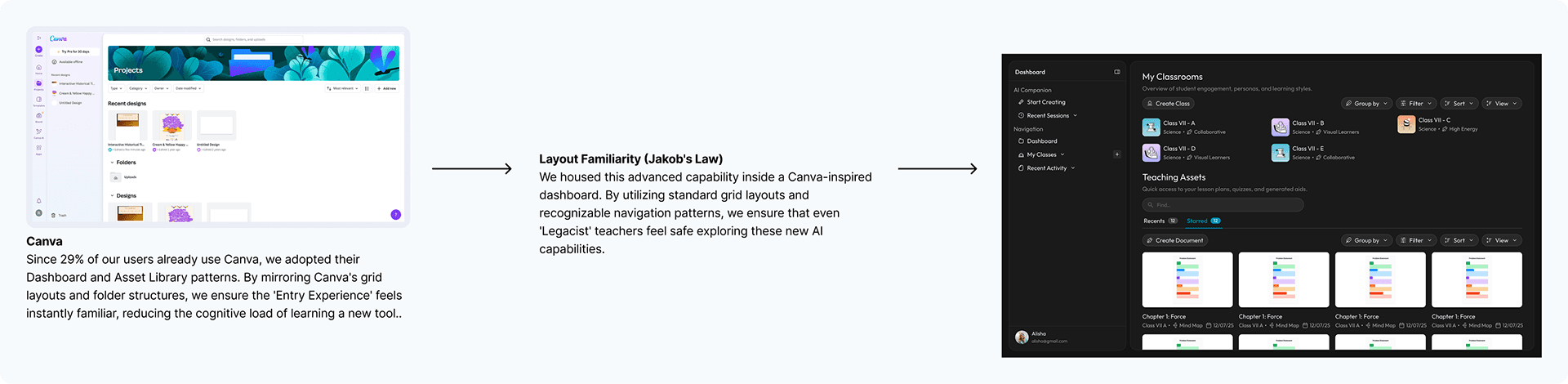
Teachers don't need better design tools; they need faster ones. While tools like Canva and ChatGPT are powerful, they fail in the classroom context because they demand high Creative Bandwidth (Prompting, Layout, Design). Aurika bridges this gap by shifting the interaction model from "Creation" (Doing it yourself) to "Curation" (Reviewing AI suggestions).
1. The Foundation (The Entry Point)
First, I ensured the 'Entry Experience' felt familiar by adopting Canva's dashboard logic — teachers already know how to navigate this ecosystem.
The Interaction Model: Shifting from Creation to Curation
2. The Interaction Model (The Brain)
Next, I solved the "Blank Page" paralysis by replacing open chatbots with Scoped Defaults — inspired by Khanmigo's structured template approach.
Feature Audit (Khanmigo)
3. The Workspace (The Editor)
For the writing interface, I adopted Notion's distraction-free editor to keep cognitive load low, while following Google NotebookLM's layout to promote multi-level task management.
Feature Audit (Google NotebookLM & Notion)
4. The Visual Engine (The "Architect" Feature)
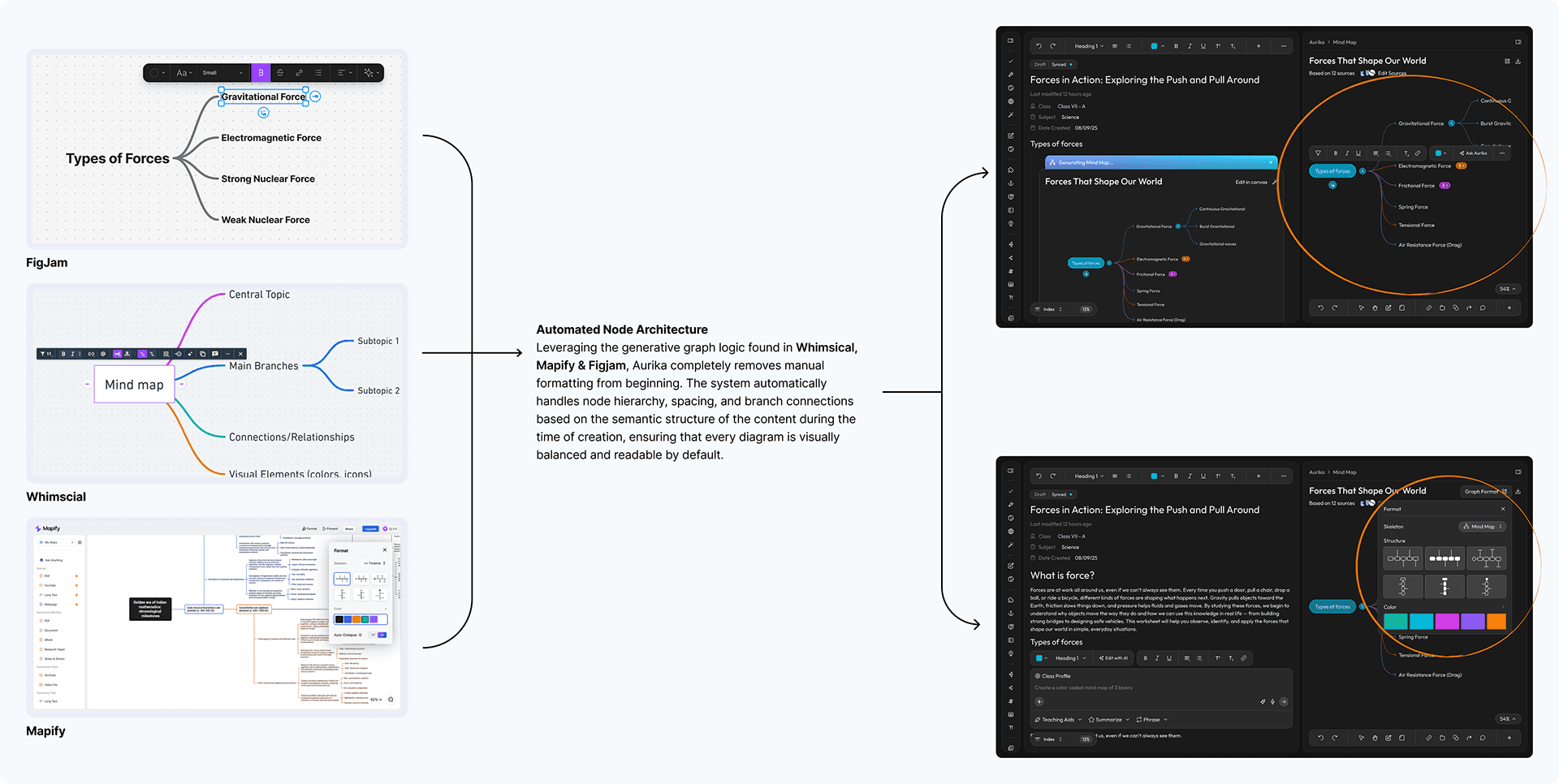
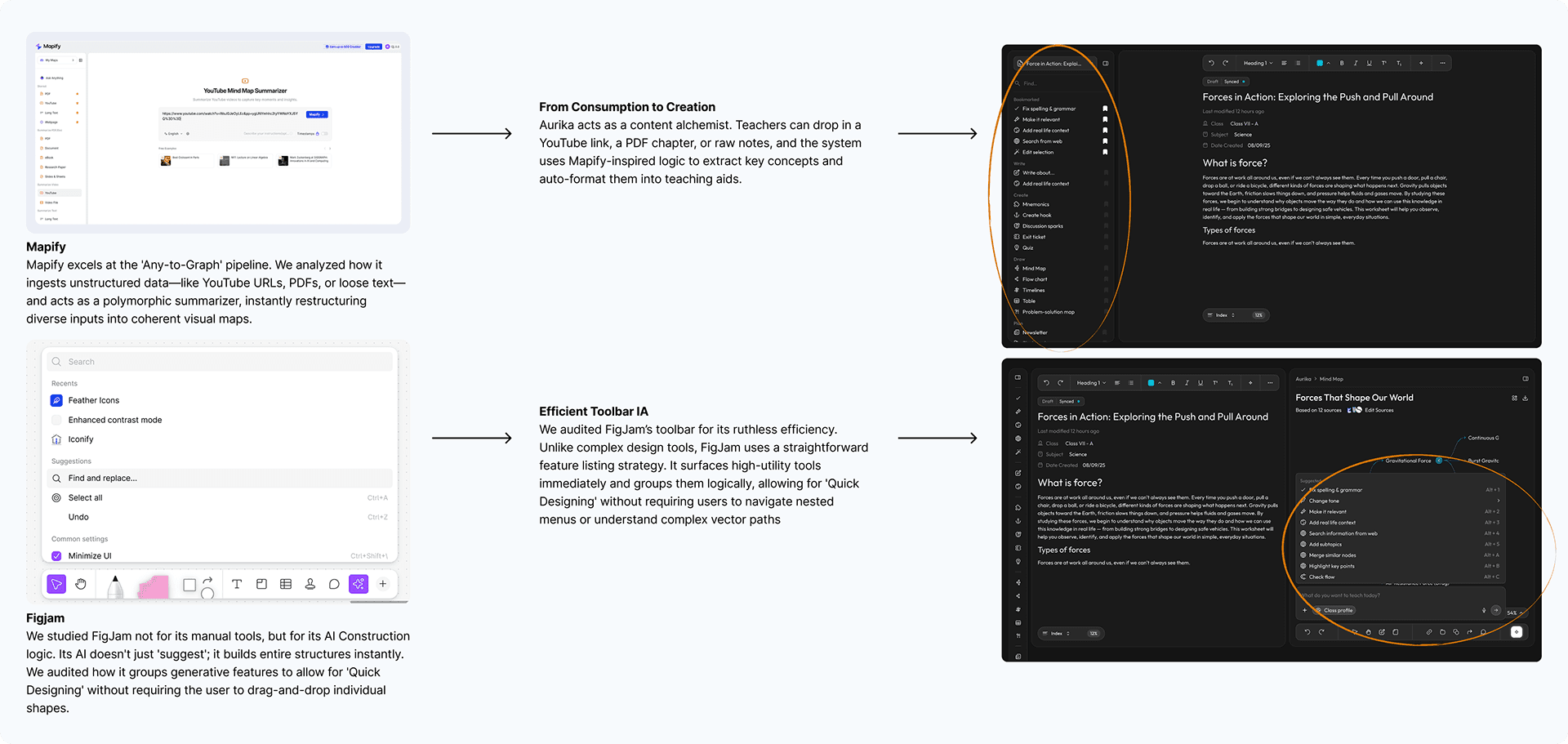
To support visual learners, I built a "Universal Visualizer" leveraging Mapify's summarization logic and FigJam's toolbar IA for automated node creation.
Feature Audit (FigJam, Whimsical & Mapify)
Feature Audit (FigJam & Mapify)
5. The Narrative Engine (The Output)
Finally, to automate the daily grind, I utilized Snapdeck's flow to auto-generate narrative-driven slides directly from lesson summaries.
Automating the narrative flow: From summary to slides
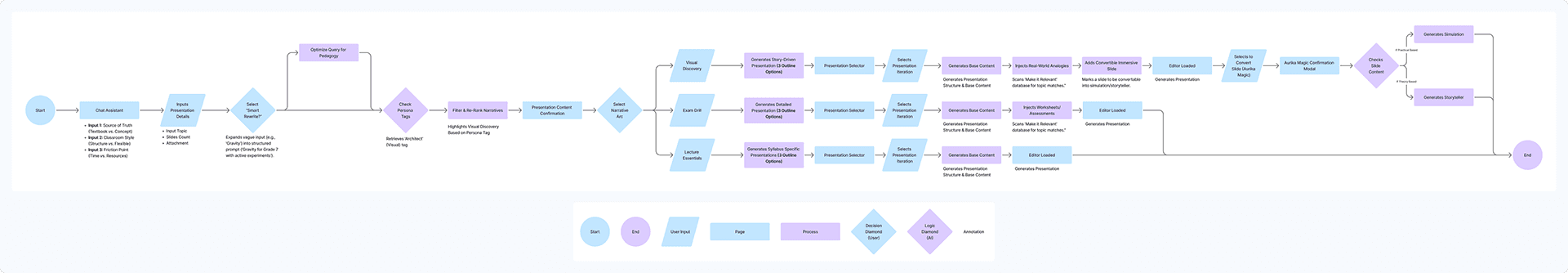
User Flows & System Architecture
Visualizing the decision trees and data pipelines that power the personalized experience.
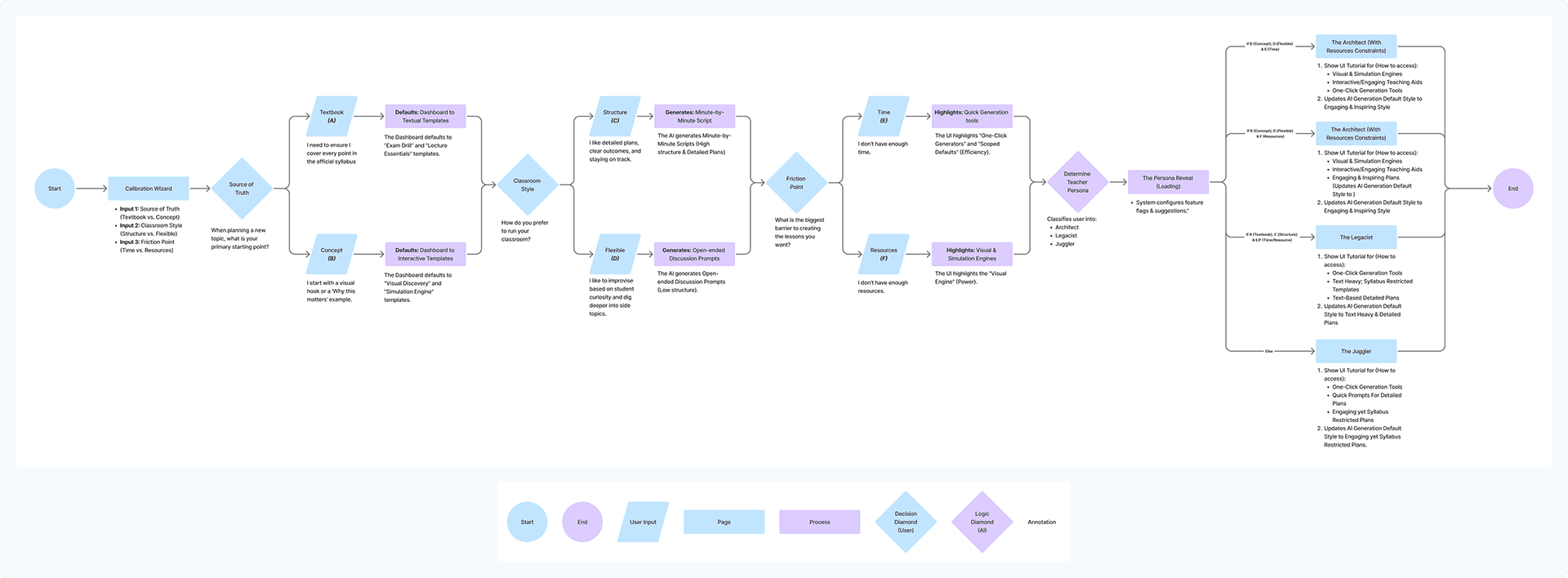
User Flow: Calibration Wizard — From persona inputs to personalized UI
User Flow: End-to-end presentation generation pipeline
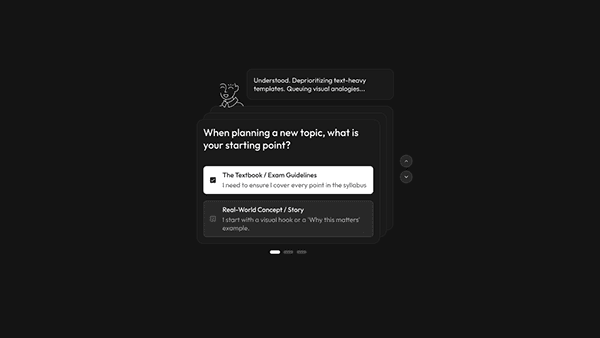
The Calibration Wizard: Personalizing the AI
Research finding: The User Archetypes study revealed four distinct teaching mindsets, each requiring a different UX approach.
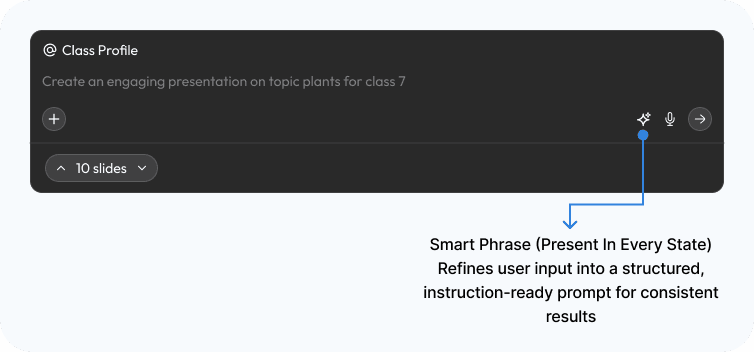
Design response: Instead of a one-size-fits-all interface, Aurika starts by interviewing the teacher to tailor the experience — capturing teaching style, subject preferences, and classroom persona to prevent "blank page syndrome" before it starts.
Based on user inputs, Aurika re-ranks the toolbar. For an "Architect" type teacher, the Simulation Engine and Immersive Storyteller are promoted to the dashboard, while text-heavy tools are deprioritized.
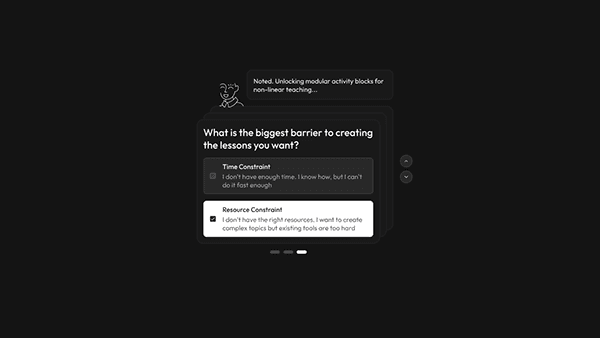
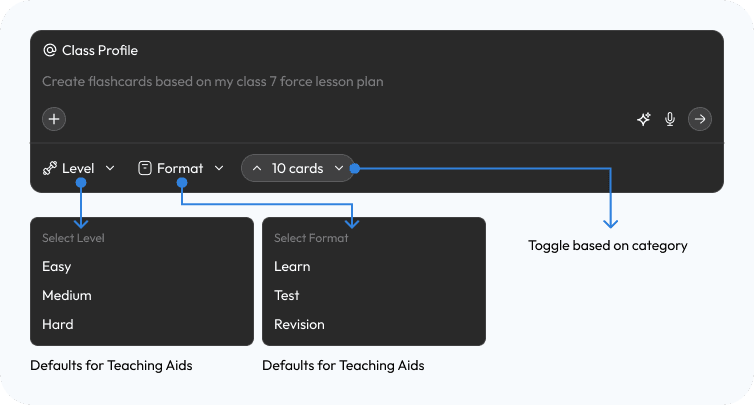
The Context-Aware Launchpad
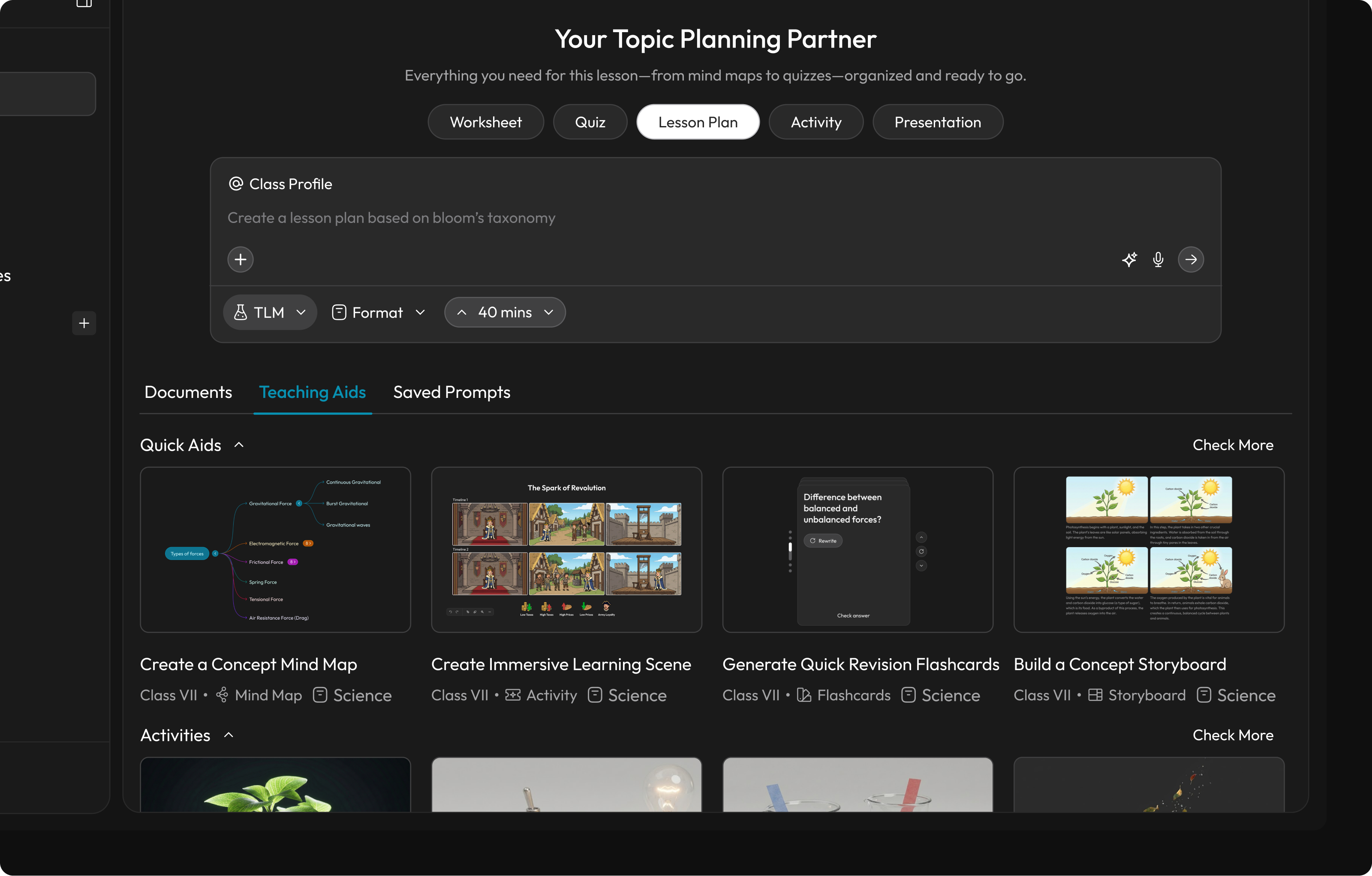
Research finding: Teachers abandon creative ideas at the execution stage because the "blank canvas" demands too many decisions upfront — leading to "Decision Fatigue" where logistics, creativity, and discipline compete for the same mental bandwidth.
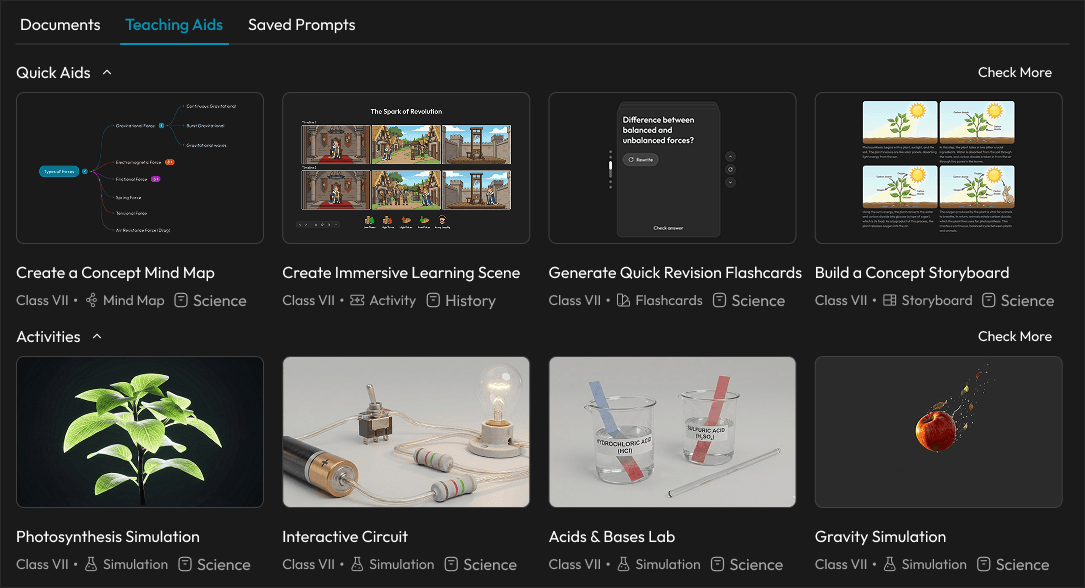
Design response: Instead of starting from zero, Aurika removes the "Blank Page" entirely. The "Quick Aids" row pre-populates context-aware tools based on the teacher's active projects and persona, while structured templates (Lesson Plans, Exit Tickets) require only minimal input to execute — eliminating decision fatigue before work begins.
Start Creating Screen
Adaptive Tool Weighting
Research finding: Teachers with strong visual or architectural instincts are forced through the same generic toolbar as everyone else—burying the simulation and storyboard tools they actually need under layers of text-centric defaults.
Design response: Recognizing the user's 'Architect' persona, the system prioritizes high-fidelity Simulation and Storyboard tools over standard text editors. Additionally, Smart Caching analyzes recent activity to proactively suggest relevant aids for current topics.
Adaptive Prompt Suggestions
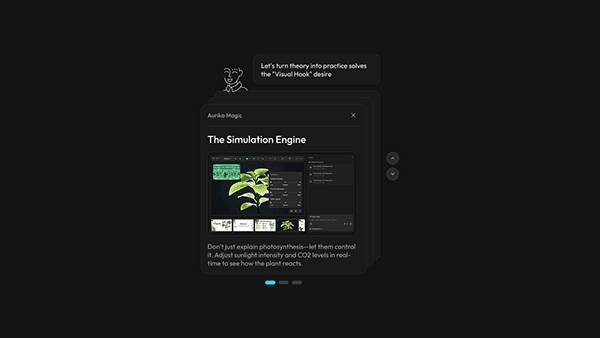
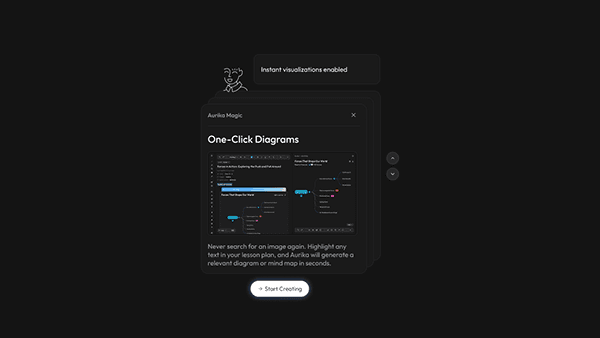
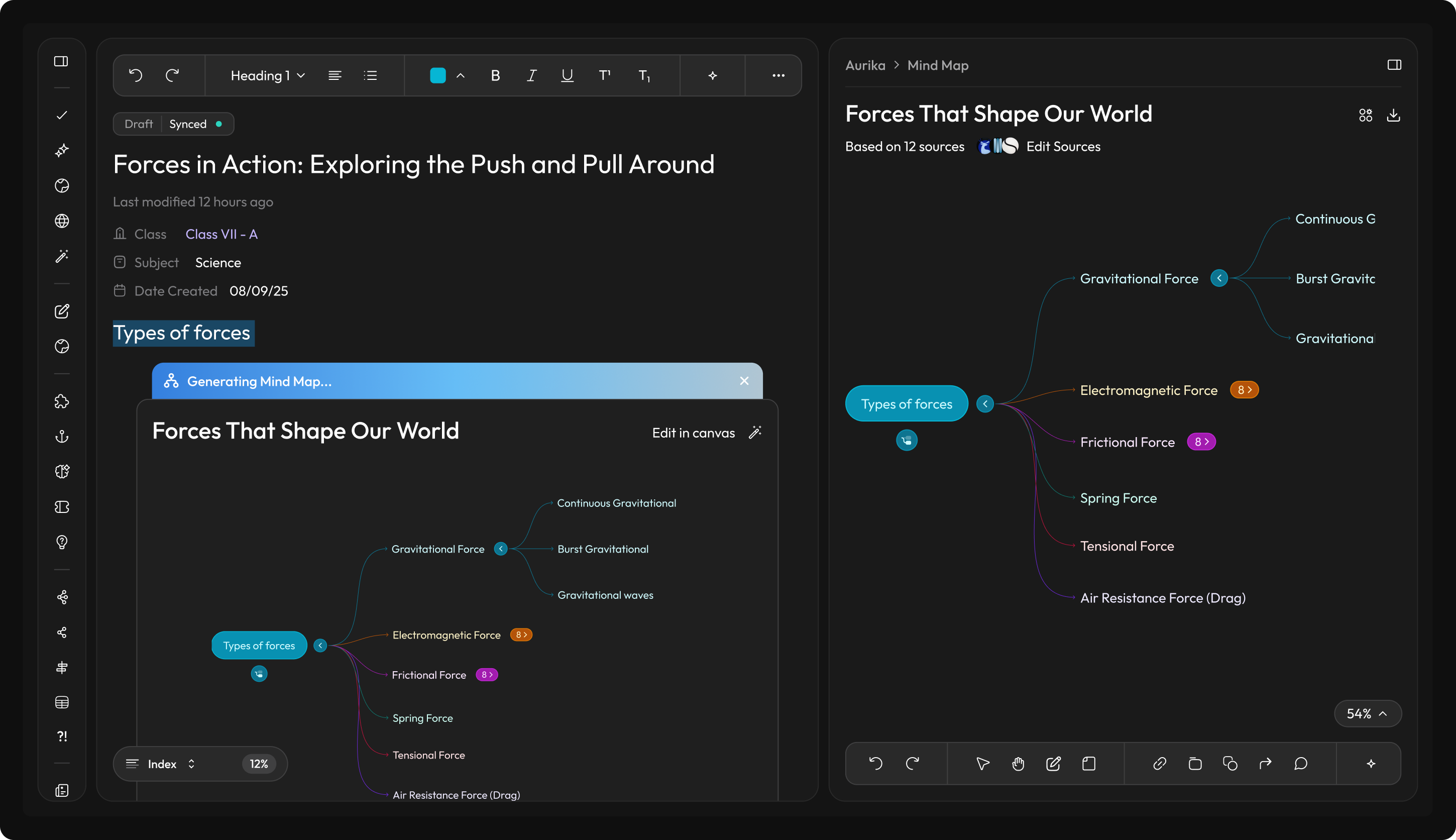
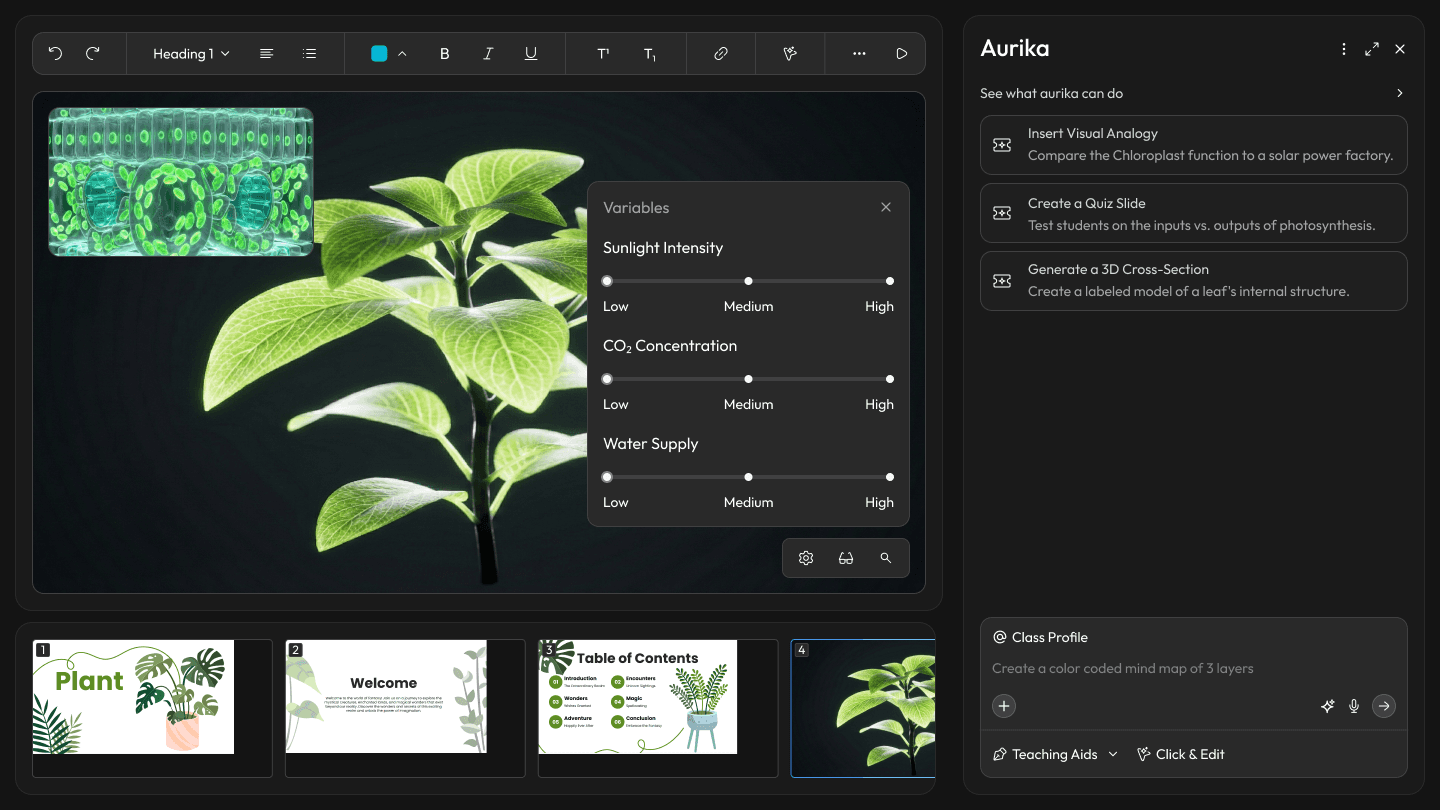
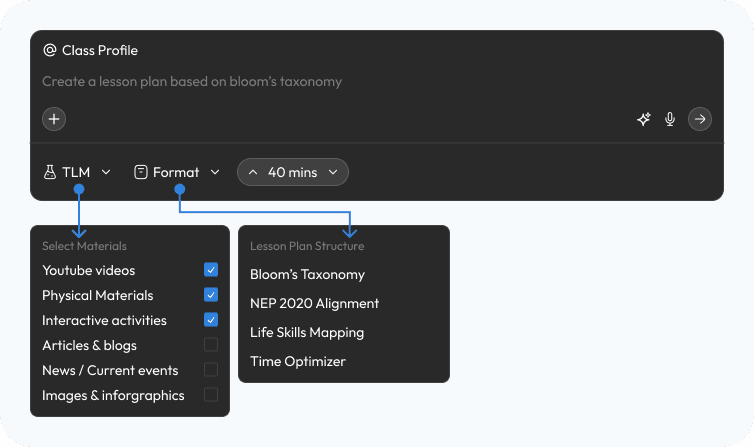
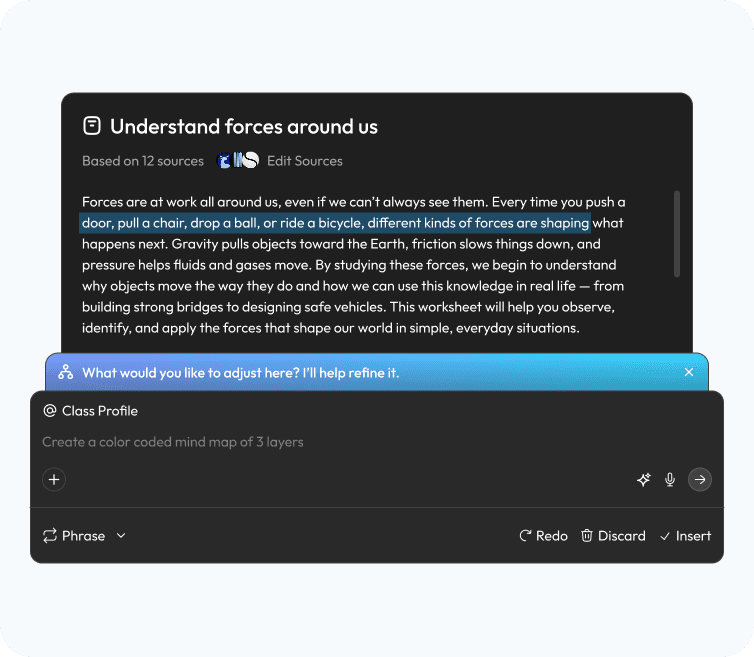
Research finding: Science is often taught as abstract theory because concepts like "Types of Forces" are delivered as static text—when they would be far better understood through activities, diagrams, and visual mind maps. But creating those materials manually takes too much logistic effort for an overworked teacher—the setup cost outweighs the benefit.
Design response: Aurika's editor actively monitors lesson content and, when it detects text that could be better represented as a diagram, mind map, or interactive activity, it suggests and generates the visual automatically. Teachers don't have to leave the writing flow—the system surfaces a "Generate Mind Map" or "Create Activity" prompt inline, turning static notes into rich visual aids with a single click.
Aurika detects lesson content and auto-generates visual aids like mind maps directly in the editor
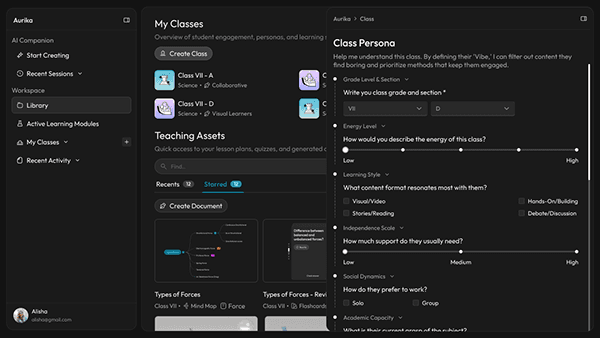
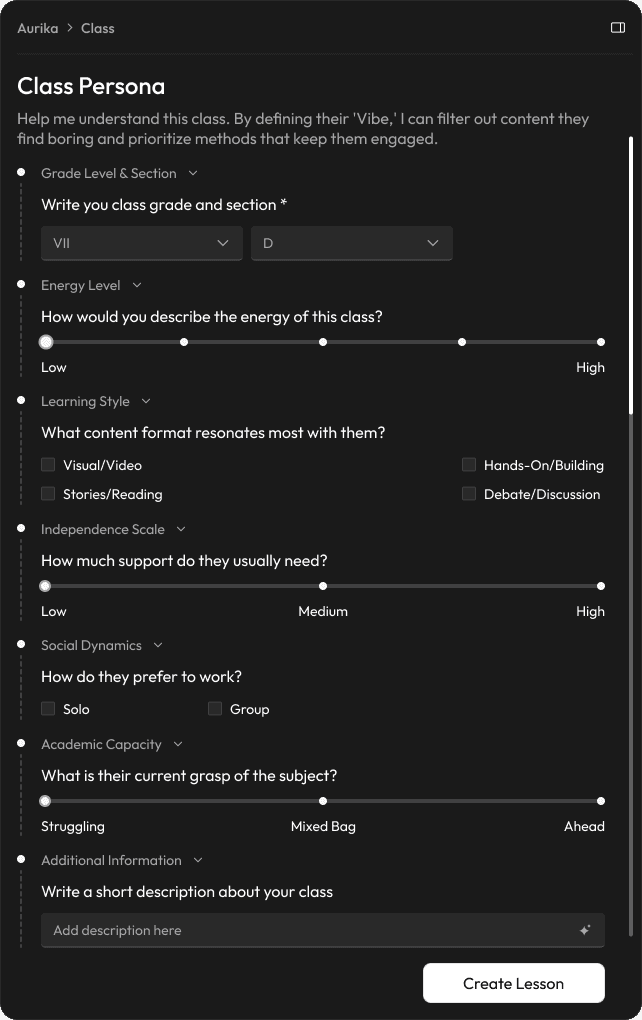
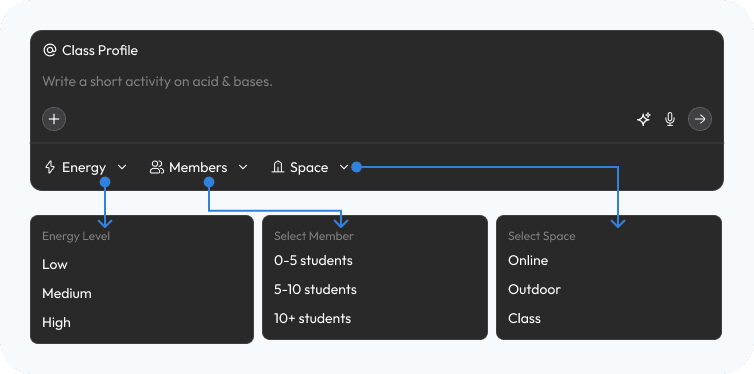
Class Persona: From Roster to Roadmap
Research finding: Standard LMS tools treat every class as a generic list of names—ignoring the behavioral dynamics that determine whether a lesson plan will land or fall flat.
Design response: Aurika introduces a calibration step, allowing teachers to input behavioral data (like energy levels and social dynamics) to generate a unique "Psychological Profile" for every section.
Qualitative Input to Pedagogical Strategy
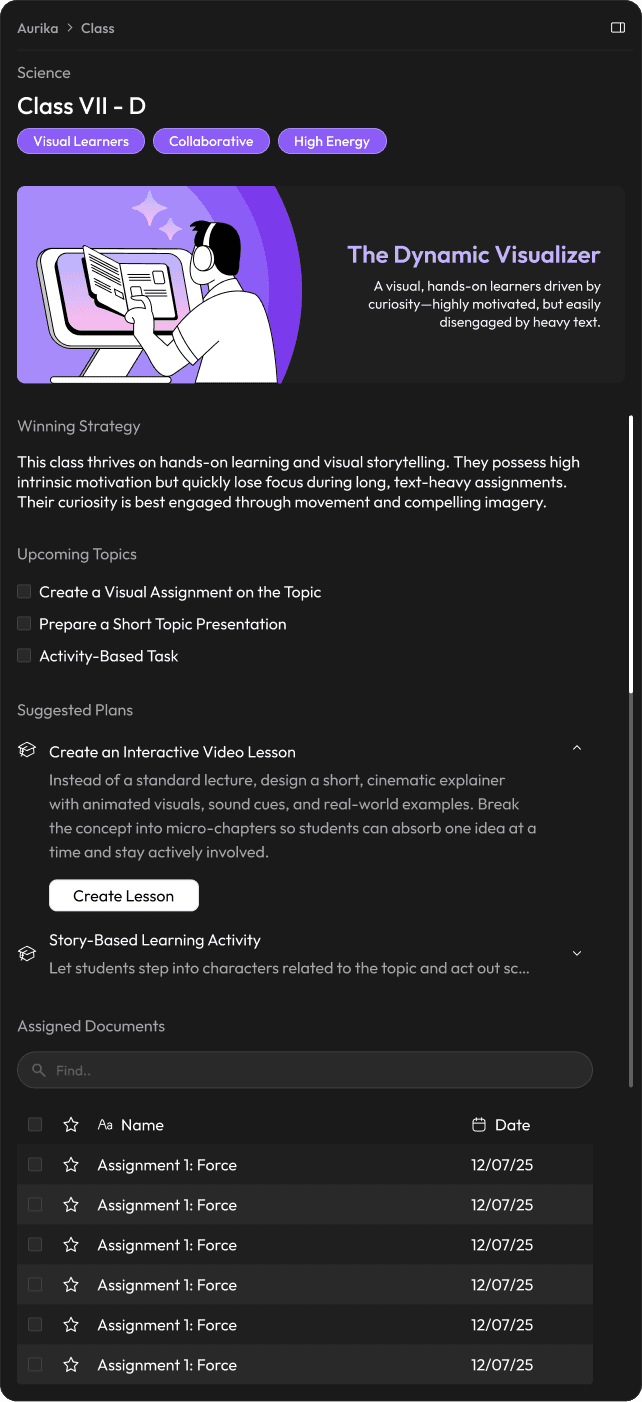
Research finding: Traditional tools track grades and attendance—hard metrics that say nothing about why a lesson failed to connect. The soft signals (energy, independence, social dynamics) that actually predict engagement go entirely uncaptured.
Design response: Aurika captures soft metrics like 'Independence Scale' and 'Social Dynamics' and analyzes them to generate a 'Winning Strategy.' For example, warning a teacher that a 'High Energy' class will likely disengage with long lectures, suggesting interactive video modules instead.
Persona Reveal Wizard
Dynamic Visual Archetypes
Research finding: Teachers walk into classrooms blind to the behavioural makeup of the group—there is no quick way to recall whether this section needs movement, debate, or quiet focus.
Design response: To reduce cognitive load, the system assigns a visual mascot to each class profile based on their dominant traits. A quick glance tells the teacher if they are walking into a room of 'Kinetic Movers' (who need activity) or 'Social Connectors' (who need debate), helping them mentally prepare before the bell rings.
The Core Workflow: From Intent to Immersion
Research finding: Teachers bounce between a chat window, a document editor, and a visual canvas—each context switch costs cognitive momentum that never comes back. The silos between planning, drafting, and visualizing force redundant work at every hand-off.
Design response: Aurika breaks the silos between Chat, Document, and Canvas. A single workflow allows a teacher to plan, draft, and visualize without ever changing contexts.
0:00
Intent — User sets parameters (Class B, Default Plan) in the Chat Assistant.
0:22
Generation — The AI drafts a structured Lesson Plan document.
0:27
Suggestion — The system detects a gap and offers an "Add Worksheet" action.
0:39
Transformation — User highlights a header and converts it to a "Mind Map," instantly switching to the Visual Editor.
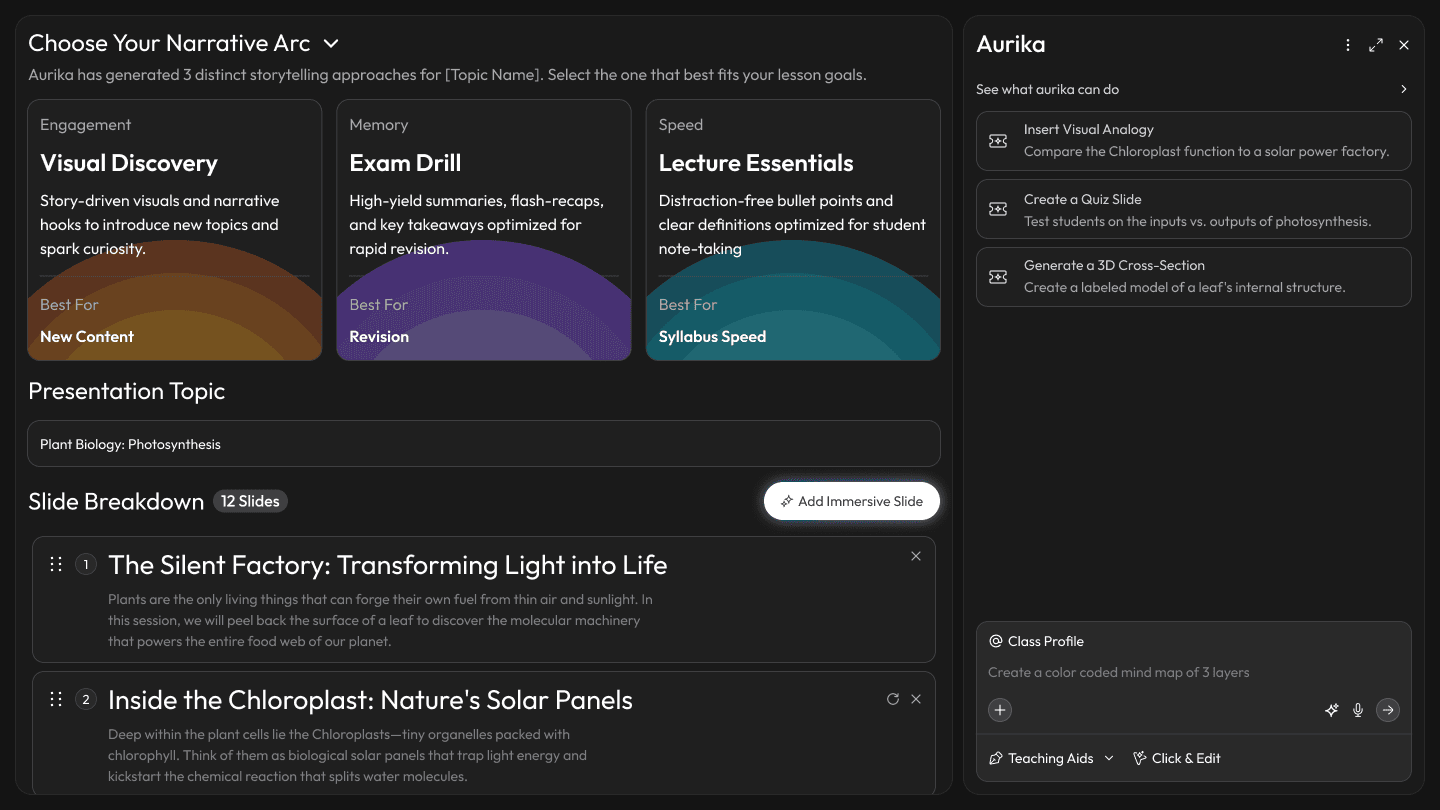
Persona-Led Structure
Research finding: Presentation tools offer the same generic structure templates to every teacher—ignoring that a visual-first 'Architect' teaching a kinetic class needs a fundamentally different narrative arc than a lecture-driven instructor.
Design response: Based on the 'Architect' calibration and the class's 'Visual' tag, Aurika bypasses the standard 'Lecture' template and prioritizes the 'Visual Discovery' arc. It also proactively suggests injecting a Simulation Slide to handle the complex topic.
Musical Classes Showcase
Topic-Specific Theming
Research finding: Teachers waste time hunting for visually relevant presentation themes—generic 'Business Blue' templates feel disconnected from Biology or History content, adding formatting fatigue on top of content creation.
Design response: The system generates topic-specific visual themes (e.g., Organic/Nature for Biology, Archive/Sepia for History) that match the lesson content—eliminating the formatting decision entirely.
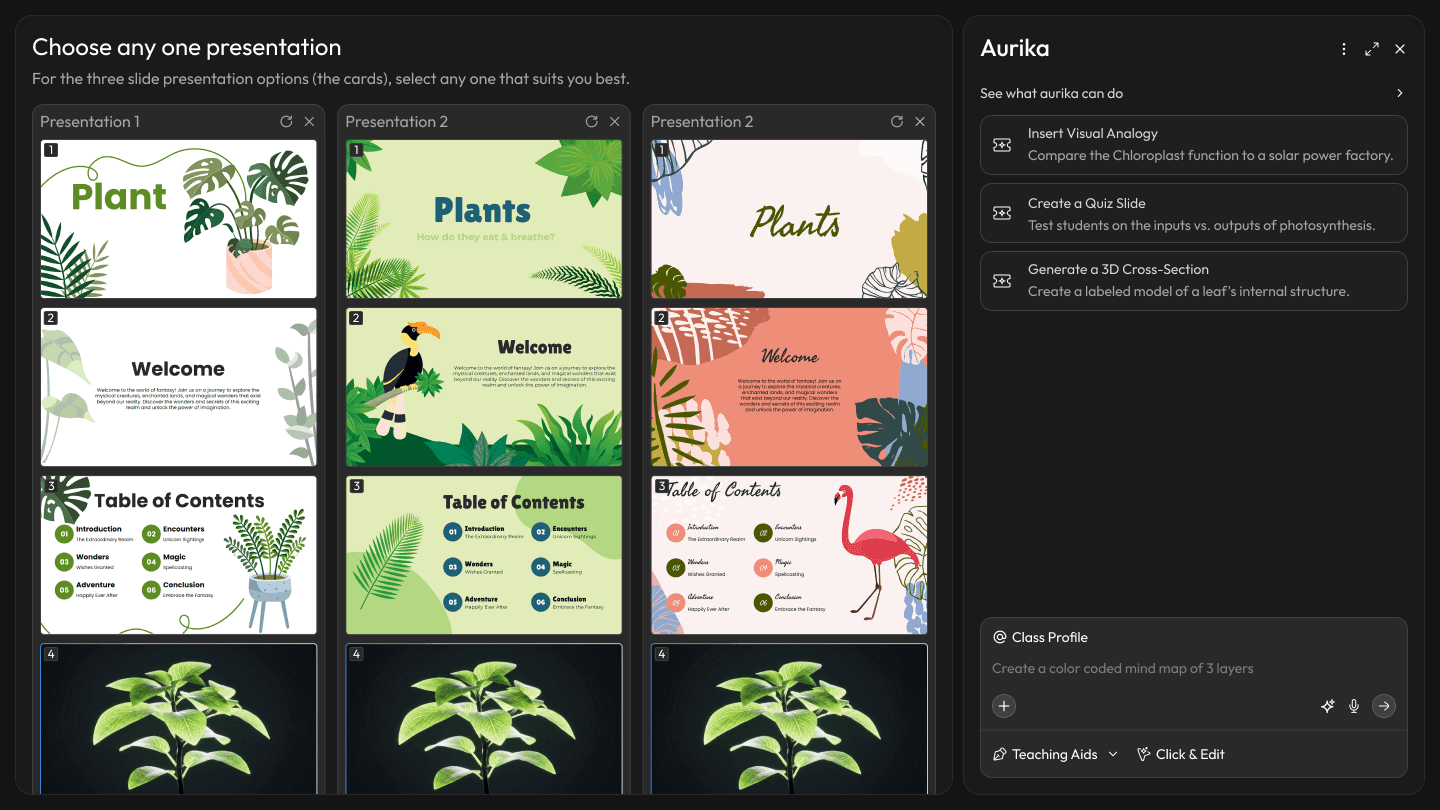
Presentation Iteration Selector
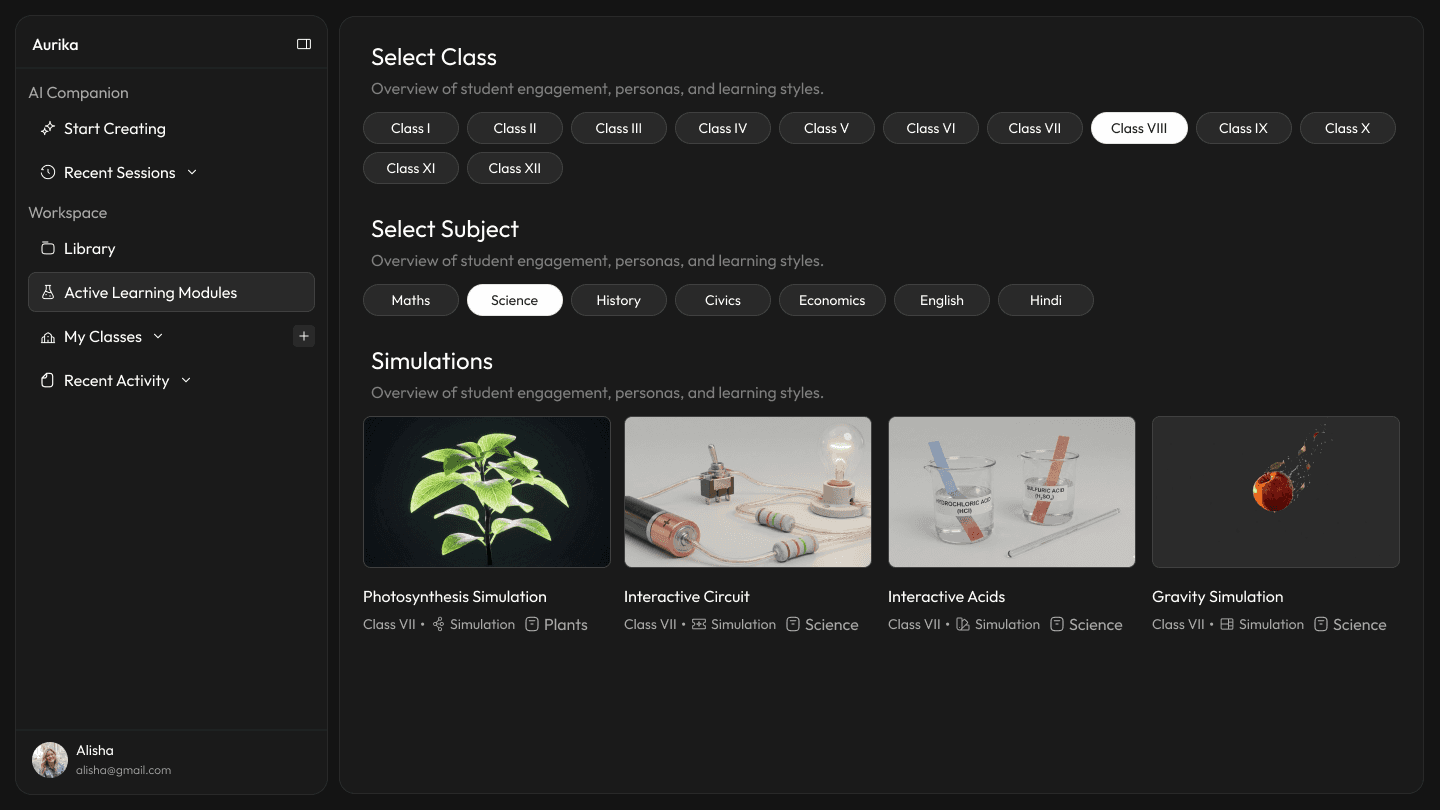
Active Learning Modules: Beyond Static Slides
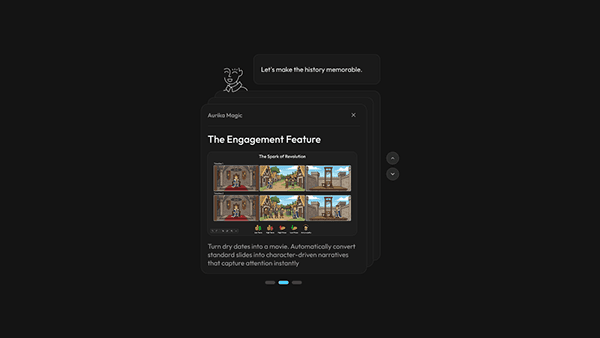
Research finding: 76% of teachers default to static PowerPoints — not because they lack creativity, but because interactive formats require too much setup time. Meanwhile, teachers know that "Stories" stick better than "Facts," but finding a relevant real-world analogy for every topic is impossible in a 40-minute prep window.
Design response: Aurika doesn't just change the content; it changes the format. The system detects the subject nature — practical vs. theoretical — and automatically swaps the module engine to match. Science gets interactive simulations; history gets narrative-driven storytelling. A built-in "Real-Life Context" generator instantly finds metaphors, historical events, or news stories related to the syllabus topic to act as Lesson Hooks.
Subject Specific Learning Engines
Universal Deployment
Research finding: Every new interactive format introduces a new interface—teachers who master a simulation tool still have to relearn controls for storytelling modules, multiplying cognitive overhead.
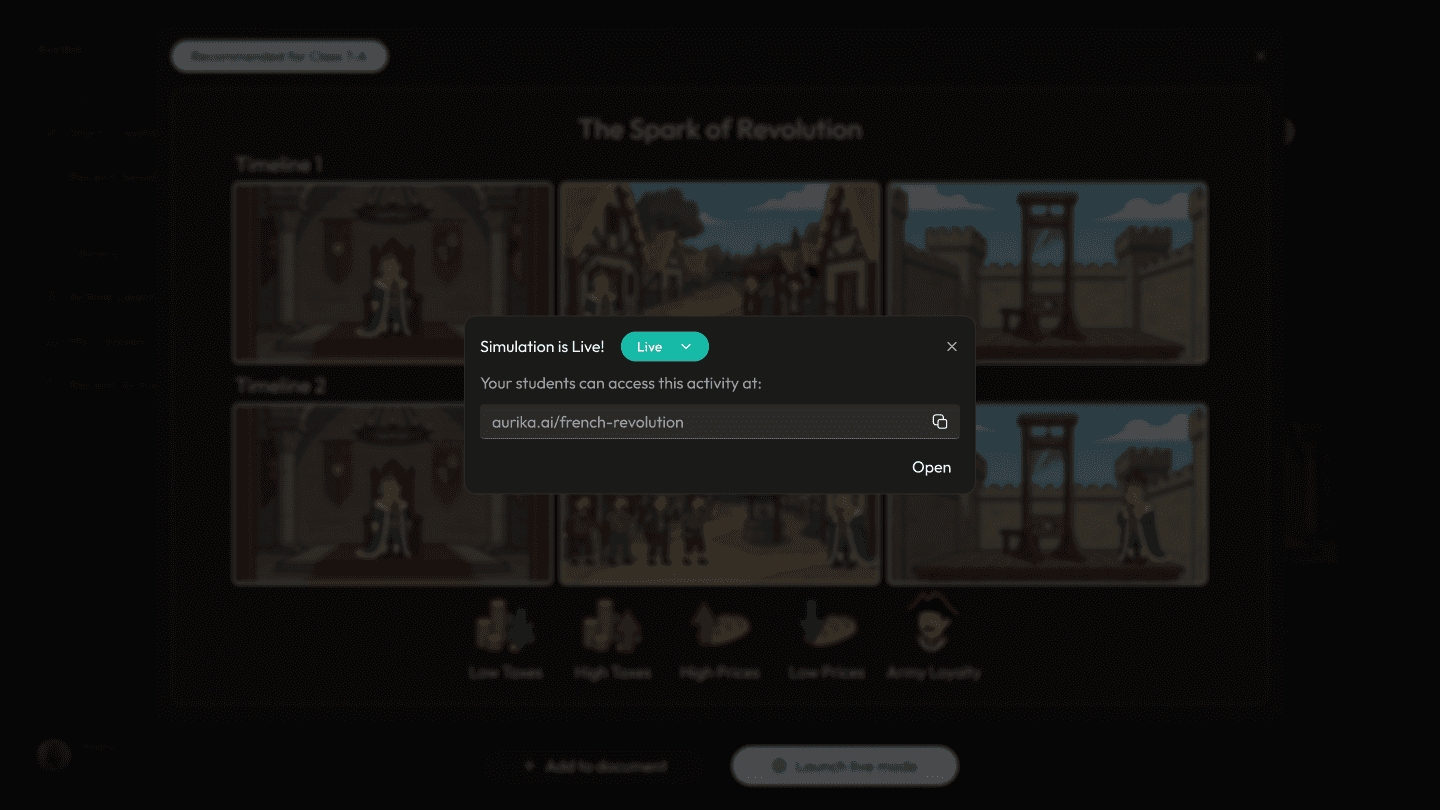
Design response: Regardless of the engine (Simulation or Story), the "Launch Live Mode" interaction remains consistent. This lowers the learning curve, allowing teachers to switch between complex Physics experiments and History roleplays without learning a new UI.
Simulation Hosting Screen
Adaptive Intelligence: Designing for Quality of Life
Research finding: Teachers constantly switch between disconnected tools—a chat window, a document editor, a visual canvas—losing context and momentum at every transition. The cognitive cost of tool-switching erodes the creative energy they need for lesson design.
Design response: Aurika reduces friction through context-aware interfaces. Whether drafting via shortcuts or directing visuals via chat, the UI morphs to fit the task—keeping teachers in a single flow.
The Text Refiner & The Visual Editor
Research finding: Editing text and editing visuals are treated as entirely separate workflows—teachers draft in one tool, then re-import and reformat in another, duplicating effort and losing fidelity.
Design response: The Chat Assistant surfaces both a Text Refiner and a Visual Editor as contextual modes within the same interface. Teachers refine copy or direct visual changes without ever leaving the conversation.
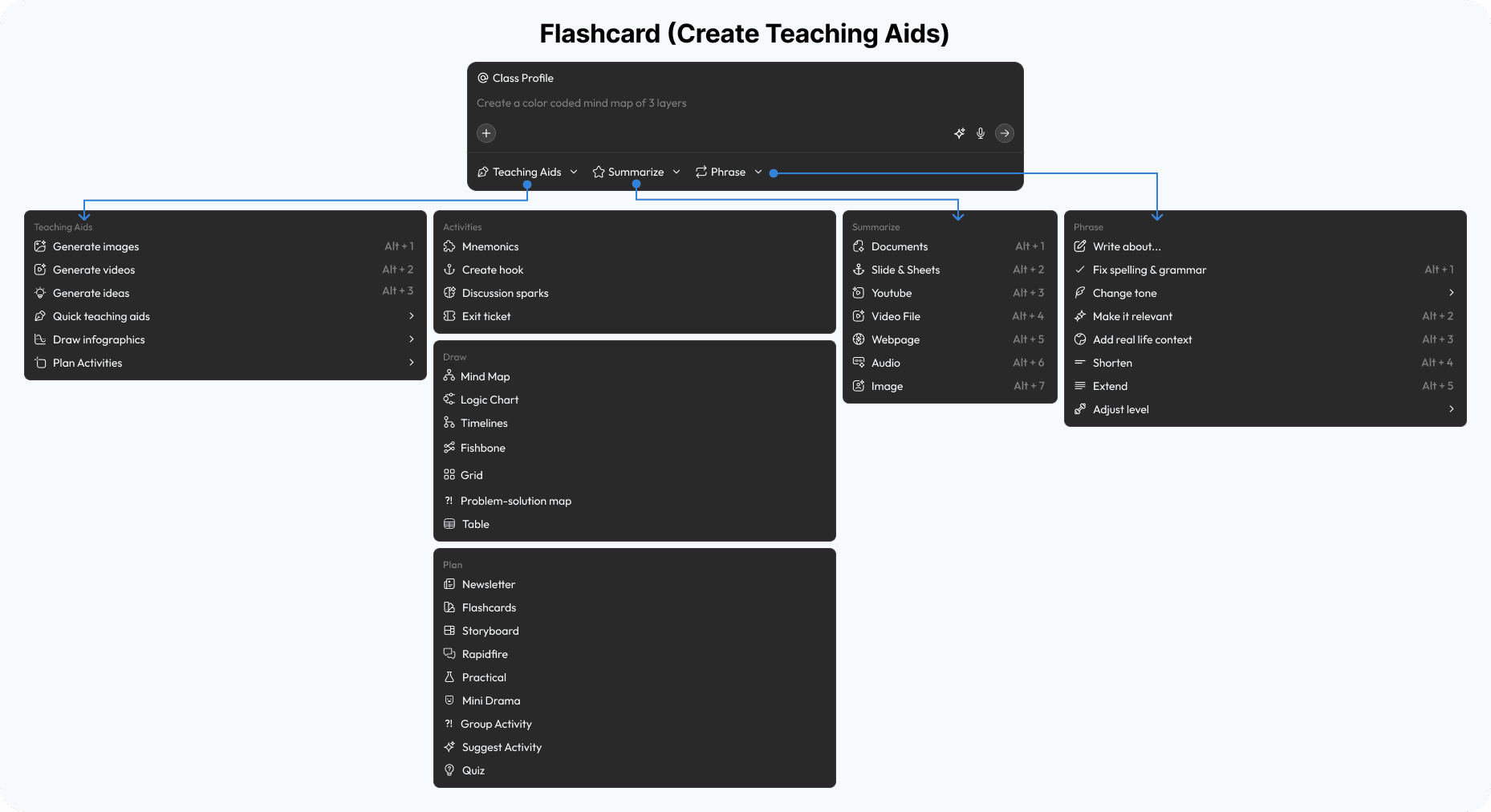
The Logic Map
Research finding: As AI-powered features multiply, the relationship between user intent and system action becomes opaque—teachers cannot predict what the tool will do, eroding trust.
Design response: A transparent architecture map connects every user intent to its executable action across the Teaching Aids ecosystem—making the system legible to both designers and educators.
Base (Chat Assistant)
Impact & Takeaways
5 → 1
Tools consolidated into a single workspace. Chat, Document, Canvas, Simulation, and Analytics unified.
4 Archetypes
Distinct teacher personas identified through research, each receiving a tailored interface configuration.
0 Blank Pages
Every workflow starts with context-aware defaults. No teacher faces an empty canvas.
Key Learnings
Future Scope
The current design addresses the core creation workflow. Here's what's next: